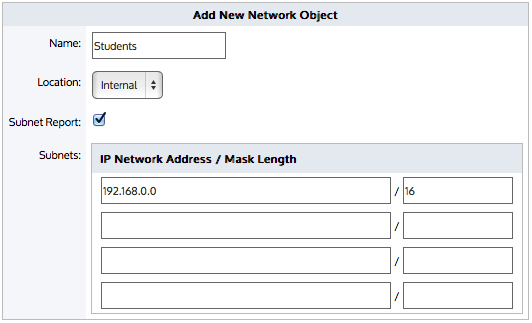
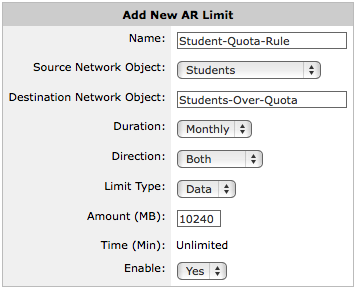
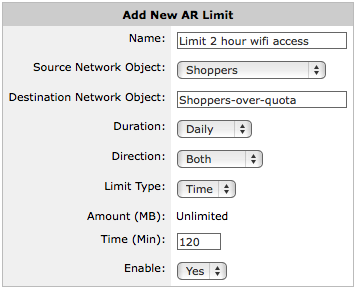
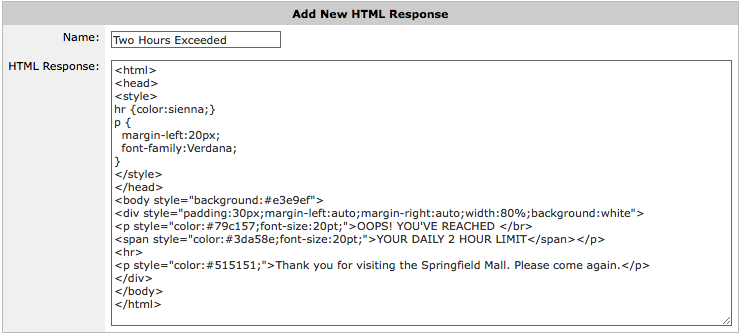
Create an adaptive response limit object to define how the quota is measured and to identify the users that have exceeded their quota by using a named network object.
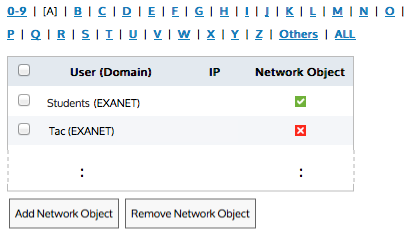
The adaptive response object can specify whether to set a network-traffic data-volume limit or a time limit. The adaptive response object identifies the traffic that is monitored against the specified quota as a network object. The network object can either be based on IP addresses, or based on Active Directory users or user groups. The adaptive response object tracks those that have exceeded their quota by dynamically adding them to a named network object.
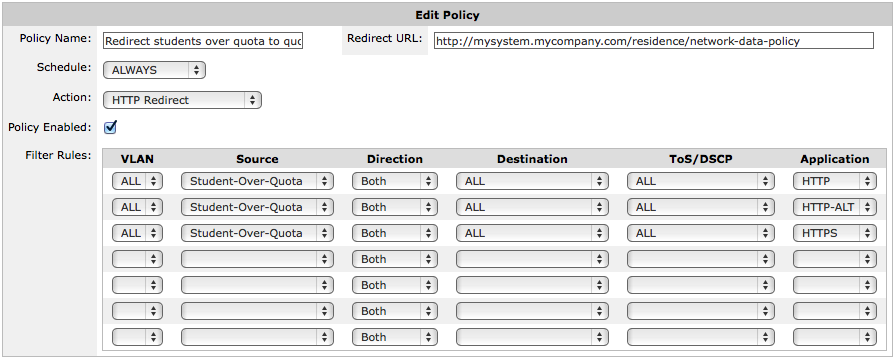
Add a policy (or policies) to the Optimizer policy tree for those who are over their limit.
The policy that addresses those that have exceeded their quota is defined according to your business needs. You can choose to throttle their traffic or block it entirely. When they have HTTP traffic, you can also choose to redirect them to a webpage that you host or respond with a webpage that the Exinda Appliance hosts.
If needed you can combine these, such that the first policy filters for HTTP traffic and then shows a webpage, but then other types of traffic are caught by a second policy that blocks the remaining traffic.
Add policies to the Optimizer policy tree for those under the limit.
The remaining policies define how to deal with the traffic of the users who have not yet exceeded their quota.
|
|
Note Since the Exinda Appliance attempts to match the traffic to the filters in the policies (and virtual circuits) in the top-down order defined in the Optimizer policy tree, you need to set up the series of policies with the most specific filter criteria appearing first in the policy tree, which means the policies should appear in the following generalized order.
|
|---|