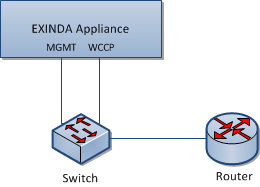
The Exinda appliance can accelerate traffic routed using Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP) v2. This topology is used when customers want application acceleration, but do not wish to install the Exinda appliance in-line.
To use WCCP v2 to route traffic to the Exinda appliance, you will need to configure both the router and the Exinda appliance. To enable WCCP on the appliance, you will use the wccp CLI command to assign an interface for WCCP. If authentication is required on the router, you can also add the router's password on the appliance. Traffic direction is determined by any configured network objects.

Some of the limitations of the WCCP out-of-path deployment include:
Access the CLI from the Web UI or via SSH, Telnet, or Serial Port in privileged (enable) mode and configure mode (configure terminal).
Assign an interface for WCCP.
For a unicast configuration, set the router IP address for each WCCP v2 service.
wccp interface <interface-name>
wccp service <service-group number> router <router-IP-address>
|
E X A M P L E Assign interface eth2 to WCCP v2 traffic with service class 10 from 192.168.0.1 wccp interface eth2 wccp service 10 router 192.168.0.1 |
|
|
Note Ensure you set the router to be the highest IP address available on the router. |
|---|
For a multicast configuration, set a group-address for WCCP v2 traffic.
(config)# wccp interface <interface-name>
(config)# wccp service <service-group number> group-address <multicast-address>
|
E X A M P L E Assign interface eth2 to WCCP v2 traffic with service class 10 from multicast address 192.168.0.1 wccp interface eth2 wccp service 10 group-address 224.1.1.1 |
If a password has been configured for a service on the router, add that password on the Exinda.
(config) # wccp service <service-group number> password <password>
For the Exinda appliance to determine traffic direction, all internal subnets should to be defined as internal Network Objects. Network objects can be edited from Configuration > Objects > Network > Network Objects.
After identifying the subnets as internal network objects, as traffic passes through the appliance, the appliance looks at the source IP and destination IP of the packet and matches them against the network objects to determine whether the source IP and destination IP should be considered internal or external, hence determining the packet direction. Consider the following rules when comparing the location of an IP packet relative to an internal network object:
|
Source IP |
Destination IP |
Result |
|---|---|---|
| Internal | External | Packet is classified as outbound traffic. |
| External | Internal | Packet is classified as inbound traffic. |
| Internal | Internal |
Traffic flowing from the lower IP to the higher IP is classified as outbound traffic. Traffic flowing from the higher IP to the lower IP is classified as inbound traffic. |
| External | External |
Traffic flowing from the lower IP to the higher IP is classified as outbound traffic. Traffic flowing from the higher IP to the lower IP is classified as inbound traffic. |
At the CLI, type show wccp service <service-group number>.
The status of the service is displayed with the Router and Appliance IP addresses. If any error messages are displayed beside an IP address, resolve the issue with the configuration and re-verify the service.
|
|
|