Virtual LAN (VLAN) Objects are used to logically separate hosts (or groups of hosts) on a functional basis rather than on a physical basis. Once VLAN Objects are defined, they can be used in Optimizer policies to filter traffic. By default, the Exinda appliance has a single VLAN defined called "ALL", which matches all traffic (regardless if that traffic is part of a VLAN or not). Additional VLAN Objects can easily be added.
All the defined VLAN objects are shown in the table. Each VLAN object can be edited or deleted by clicking the appropriate button in the table. The ALL VLAN object is protected and cannot be edited or deleted.

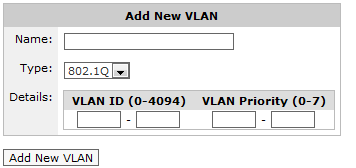
Go to Configuration > Objects > VLANs.
Specify the range of VLAN IDs to define.
To define all VLAN IDs, leave this field blank or type 0 - 4094. A single VLAN ID can be defined by entering the same value in both fields.
Specify the VLAN Priority range to define.
To define all VLAN Priorities, leave this field blank or type 0 - 7. A single VLAN Priority can be defined by entering the same value in both fields.
Click the Add New VLAN button.
The VLAN will be added to the list of VLANs in the table.
|
E X A M P L E Consider VoIP traffic that has a VLAN ID of 10. Create a VLAN object with this ID. This object can then be used to prioritize VoIP traffic using the Optimizer. Name: VoIP The VLAN priority is a field in the 802.1Q header that networking devices use for their own QoS-purpose. In order for the VLAN Object to work properly, the VLAN Priority field indicated in the object must match the Priority set in the 802.1Q header. If the priority set for a specific VLAN is unknown, Exinda recommends to configure the VLAN priority inside the VLAN object as “0 – 7”, which covers all possible scenarios. For most networking vendors, if the VLAN priority was not specified, the packets are tagged with Priority 0 by default. |
|
|
|