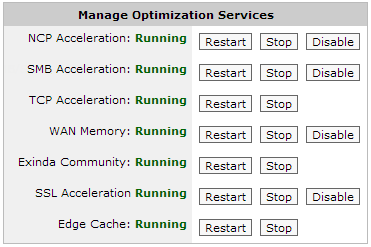
Edge Cache – Provides acceleration of static web content such as HTML, GIF, JPEG, ZIP, RAR, ISO as well as dynamic content including YouTube, Google Video, Vimeo.
|
|
Note The Acceleration feature (including universal & protocol-specific acceleration) is licensed separately. Edge Cache is also licensed separately. Please contact your local Exinda representative if you wish to enable either of these features. |
|---|